No matter how old or young you are, we are all susceptible to acute and chronic medical conditions. Both conditions differ in how long they last and how severe the diagnosis is. An illness or condition can be as simple as the flu, or in a more severe case cancer or arthritis.
Whether it is an acute or chronic medical condition you are facing, it is important to know the difference between the two, so that you may know when it is the right time to immediately seek medical treatment. However, a chronic medical condition diagnosis would typically lead you to take time to find a treatment plan that will help you for the rest of your life.

What Is The Difference Between Acute And Chronic Medical Conditions?
Acute medical conditions typically develop over a short period of time1. This can be anywhere from days to weeks and generally be resolved in less than six months1. Acute illness is usually formed by a virus or infection. In some cases, the misuse of drugs/medication, falls or car accidents can be the cause of an acute medical condition1.
A chronic medical condition will tend to develop over a longer period of time and may intensify over months or years.1 Chronic illness can be caused by unhealthy habits like poor nutrition, lack of exercise, misuse of alcohol, and smoking or vaping1.
What Are Some Examples Of Acute And Chronic Medical Conditions?
The flu, rotavirus, infections like pink eye or urinary tract infections, and broken bones are examples of acute medical conditions. In some cases, acute medical conditions may require medical intervention2. These conditions include pneumonia, appendicitis, pancreatitis, or acute liver or renal failure.
Chronic illnesses can be tough to identify. For example, you may feel some minor restrictions with your joints before you realise you have arthritis. Until the joint pain has become unbearable, you would look to seek further medical attention and may be diagnosed. Other symptoms of arthritis include visible inflammation around the joints and warm red skin over the affected joint2. Daily tasks will be restricted due to incapacitation from arthritis.
Another example of chronic illness is diabetes. Initially, you may be feeling thirsty or need to have frequent urination and in some cases, people may have no symptoms at all. As the disease grows, complications are highly likely to occur. These include neuropathy, kidney disease, and high blood pressure. Both of these chronic conditions have long-lasting implications and they have no possible way of preventing the illness from occurring2.
What Is More Severe, An Acute Or Chronic Medical Condition?
Chronic illness is considered more severe than acute illness. This is due to chronic illness having a slower but long-term effect on your health and well-being, with some chronic illnesses lasting for months, years, and even a lifetime. In comparison to acute illness, chronic illness will never completely heal on its own and a patient may never recover completely. In some cases, the condition can be life-threatening, with examples including heart disease and stroke. Other illnesses such as diabetes and cancer may stay for longer periods3.
However, it does depend on each patient’s circumstances and diagnosis. Chronic leukaemia may last for years and give the patient the opportunity to live their life with freedom. In other cases such as acute leukaemia, the disease will spread at rapid speed, forcing the patient to choose a treatment plan at the first sign of symptoms4.
It is important to be aware of your health, well-being, and habits affecting your health. By doing this you can achieve a life of longevity and good well-being.
How Are Acute Or Chronic Medical Conditions Treated?
A patient with a chronic medical condition will need to manage their illness over a long period, maybe the rest of their lives. By choosing to manage the condition you can prolong their life and its quality. This can be done by making regular appointments with their GP (General Practitioner) or Specialist, taking their prescribed medication, and following their treatment plan. A patient can also improve their condition by choosing to create a healthy lifestyle by introducing good nutrition, exercise, and getting sufficient sleep2.
For example, a leukaemia patient would need a treatment plan personalised to the type of leukaemia they have, and how advanced it is at the time of the diagnosis. The patient may also want a second opinion as it is always good to understand what their options are before beginning treatment4.
With an acute medical condition, the illness will occur quickly and require assistance and treatment at the first sight of a diagnosis. Once the illness or condition is treated the symptoms may be remedied. Breaking a bone is an example of an acute medical condition that may need to be seen by a doctor and will heal on its own. In some cases, acute conditions like a broken bone or a common cold will heal on their own. This does not ultimately mean every time an acute medical condition occurs there is the certainty it will heal on its own. Alternatively, you may need to make regular visits to your GP to have checkups and take protective measures1.
References
- 2020, https://www.ncoa.org/article/chronic-versus-acute-disease, National council on aging
- Nicklya Harris-Ray, 2022, https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/difference-between-acute-and-chronic-illnesses#091e9c5e8241a97a-2-7, WebMD
- 2021, https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/chronic-illness, Better Health Channel
- Majorie Hecht, 2022, https://www.healthline.com/health/chronic-vs-acute-leukemia#types, Healthline
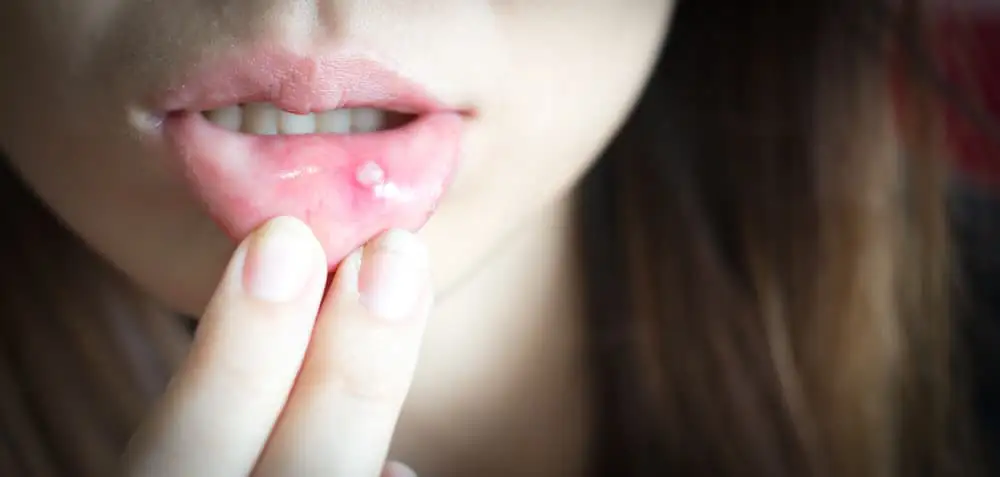
What Causes Mouth Ulcers? How To Treat & Prevent Them Effectively
Mouth ulcers are a common oral condition that affect most people at some point in their lives. They can be uncomfortable, but they are usually harmless and will heal within 10 to 14 days without treatment. Here’s everything you need to know about mouth ulcers, including what they are, what causes them, the best treatments,…
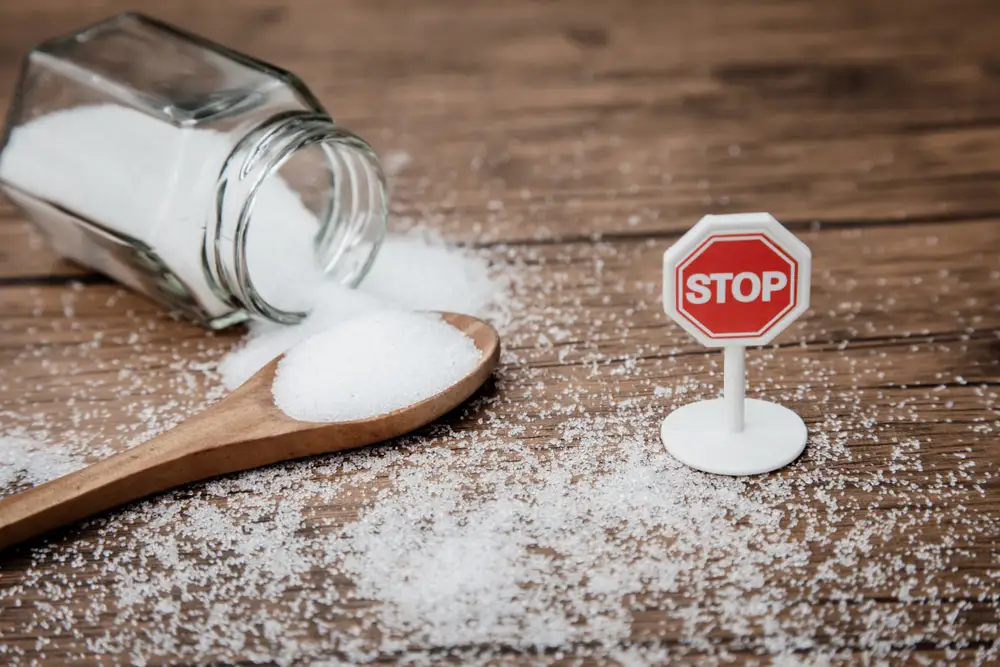
How Much Sugar Per Day?
Sugar is a type of carbohydrate and a source of energy for our bodies. It can occur naturally in foods like fructose in fruit, glucose in fruits and vegetables, and maltose in wheat and barley. However, manufacturers also often add sugar to extend the shelf life of foods, improve their appearance and/or make them taste…
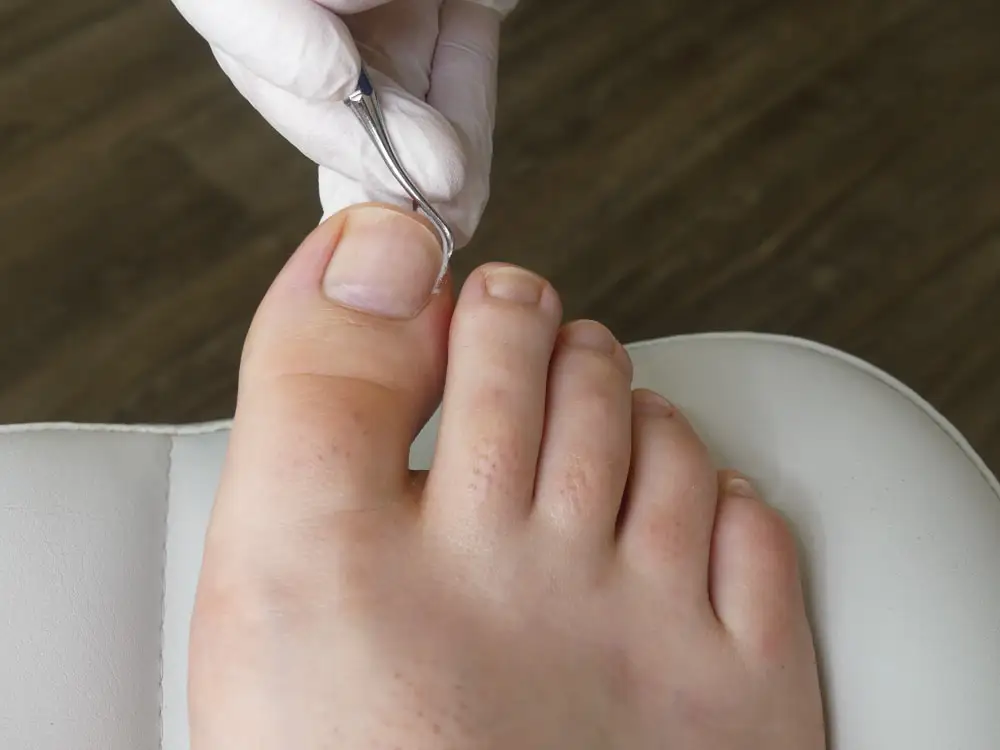
How To Fix Ingrown Toenails
Ingrown toenails occur when the corner or edge of a toenail curves and breaks through the skin of the nail and the skin surrounding the nail. It is a common condition and typically affects the big toe. If it becomes infected (you notice pus or fluid) and is left untreated, it can spread and infect…